6: Creating a Process in C
Table of Contents
This lab shows how to create a process in Windows using the system call
CreateProcess(). More information on Microsoft’s site:
Please create a file called lab6.c from the
template C file for this assignment.
6.1. Creating a Process
Creating a process in Windows is a multi-step process:
Create the variables
Allocate memory
Call
CreateProcess()Release the process handles
CreateProcess() requires several important parameters.
The full path to the application or program to execute.
Pointer to
STARTUPINFOstruct.Note
You must allocate the memory required for the struct.
Pointer to PROCESS_INFORMATION struct.
Here is the full parameter list for CreateProcess().
CreateProcess() Template Code
Required Include Files
#include <windows.h>
Example Usages
char exe_path[] = "C:\\Windows\\system32\\notepad.exe"; STARTUPINFO startup_info; PROCESS_INFORMATION process_info; BOOL process_status = FALSE; // allocate memory and clear memory ZeroMemory(&startup_info, sizeof(startup_info)); startup_info.cb = sizeof(startup_info); ZeroMemory(&process_info, sizeof(process_info)); process_status = CreateProcess( NULL, // Use the command line arg instead exe_path, // path to exe using command line NULL, // Process handle not inheritable NULL, // Thread handle not inheritable FALSE, // Set handle inheritance to FALSE 0, // No creation flags NULL, // Use parent's environment block NULL, // Use parent's starting directory &startup_info, // Pointer to STARTUPINFO structure &process_info); // Pointer to PROCESS_INFORMATION structure /* Do work with handles */ // Close process handles and clean up CloseHandle(process_info.hProcess); CloseHandle(process_info.hThread);
6.1.1. Task
Your first task is to create a process and verify the process status.
Create a new process for notepad.exe.
Verify if that process created successfully by evaluating the return
boolflag.Close the process handles.
Print an error message with the file path and exit the program with
return 1if the process did not start.
Expected Output
// Failure
Error. Failed to execute C:\\Windows\\system64\\invalid\_file.exe.
// Success
A new Notepad opened.
6.2. Process Information
PROCESS_INFORMATION struct contains these fields:
typedef struct _PROCESS_INFORMATION {
HANDLE hProcess;
HANDLE hThread;
DWORD dwProcessId;
DWORD dwThreadId;
} PROCESS_INFORMATION, *PPROCESS_INFORMATION, *LPPROCESS_INFORMATION;
6.2.1. Task
Print the process ID of the process
Expected Output
Created a new process with ID 14156.
6.3. Waiting for the Process to Exit
At this point, your program created a new child process and then exited immediately. We can observe the behavior by using the sleep function to watch the process change parents from your program to root.
6.3.1. Task
Download and then start Process Explorer.
Use the sleep function to pause your program for 15-20 seconds.
Sleep(15000);
Find your application in the Process Explorer list. Click on the child process to highlight it.|br|

Watch what happens when your application exits.|br|
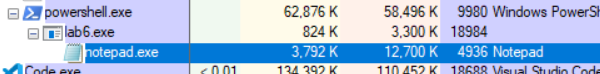
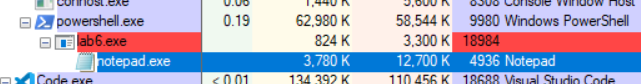
Instead of exiting or processing additional code, the parent program can
use WaitForSingleObject() to wait on the child to complete its work
and then terminate.
// The second field is milliseconds for a set time or INFINITE WaitForSingleObject( process_info.hProcess, INFINITE );
Add function
WaitForSingleObject().Your program should stay active until you close the Notepad window.